In the prior post we have built the history layer, now it is the time to look into its data. The idea is to get some simple interface providing interactive access to any data we want. Let’s try to achieve that with the leading open source software for time series analytics, Grafana.
Installation
I installed Grafana on my development machine using Docker. How to install Docker can be found here.
With Docker ready, you can install Grafana
sudo docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name=grafana -v /opt/grafana:/var/lib/grafana grafana/grafana
sudo docker update --restart=always grafana
Of course, there is also standard installation
Grafana Dashboard
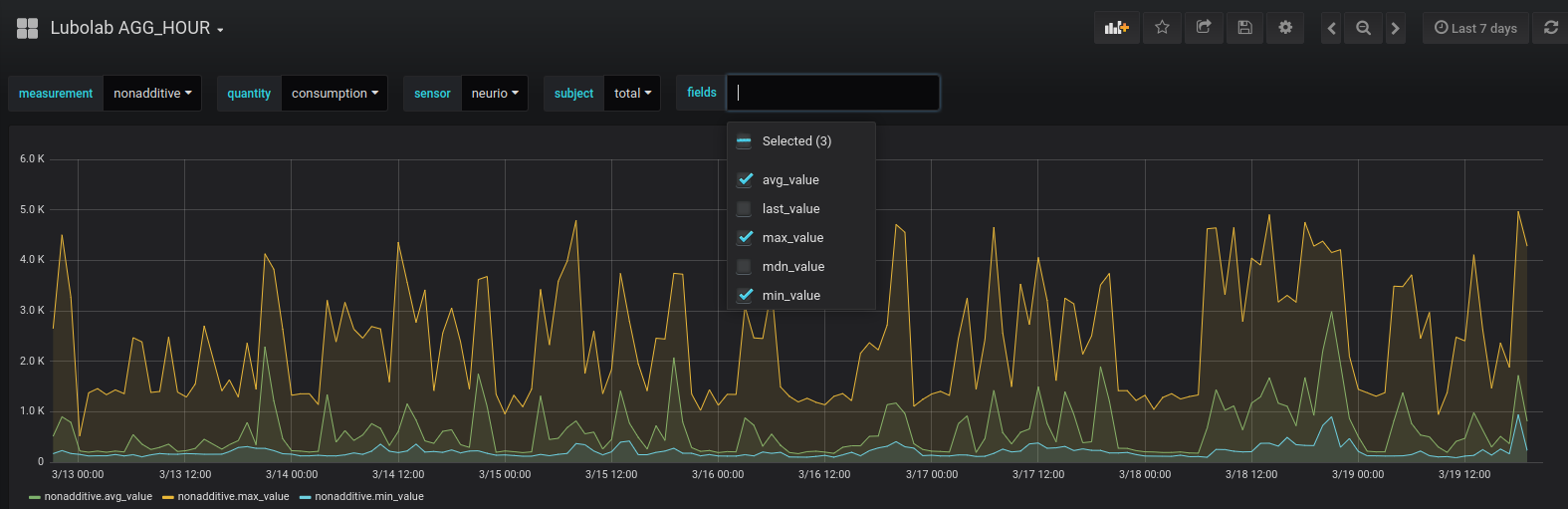
I want to make a dashboard having only one graf panel which can show any data based on the selection criteria given by a set of drop-down select boxes.
Let’s check the data structure of the hourly aggregated database to get a better idea what selection criteria we need.
use agg_hour
show series limit 1
which gives us this
key
---
additive,quantity=event_count,sensor=carpinus,subject=push
So for our dynamic dashboard, we need to define select boxes for:
- measurement
- quantity
- sensor
- subject
- multiple metric fields
In Grafana we need to introduce a variable for any such selection box. And we can use already defined variables within another variable definition. This way any dropdown list provides only values applicable in the particular context of related selections.
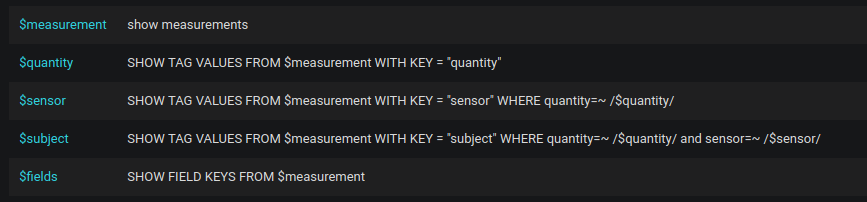
Having all needed variables defined, we can compose the query providing the data for the visualisation.
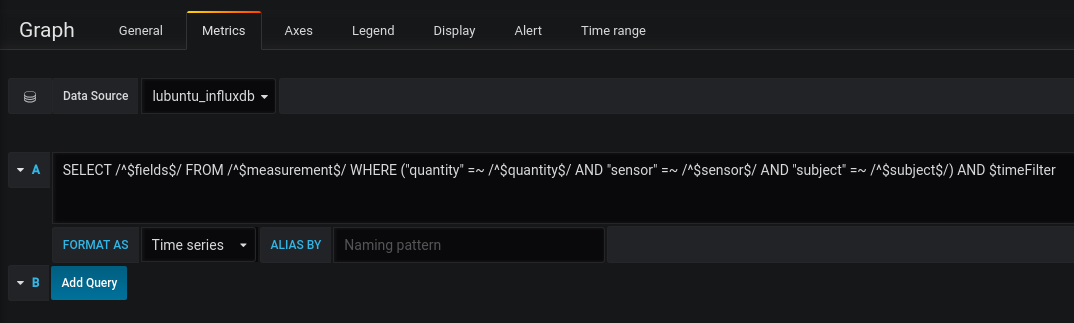
Having all that in place, we can visualize any data available in the agg_hour database. The time filter is added to the end of the query by Grafana and it is sort of internal variable which is shown as drop-down select box at the top-right corner of the dashboard.