Personal environment
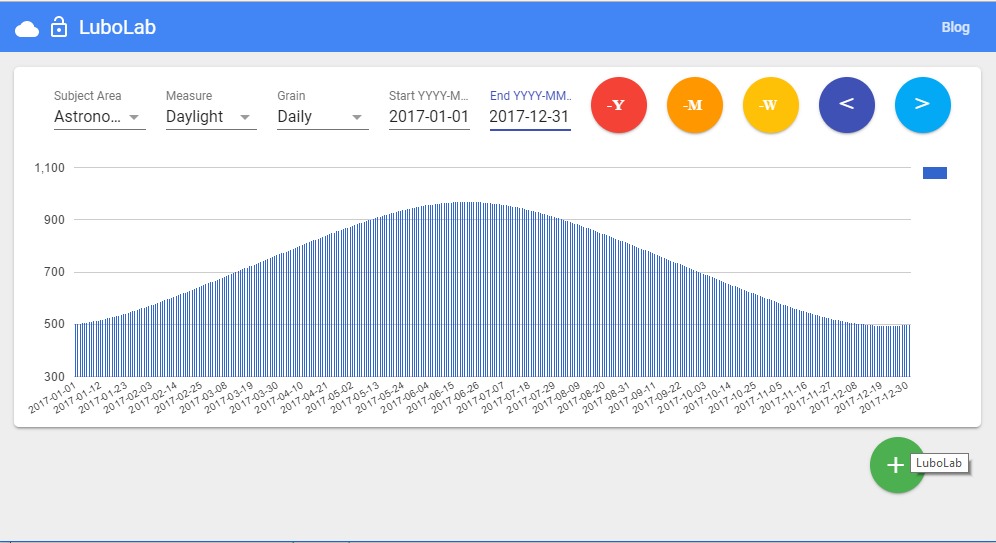
Personal DWH begins with data about personal environment. Weather and day length affect our activity significantly. We already have Weather Data mart created, so now it is the time to build another one on top of astronomical events.
The detail layer
We start in our detail layer, focusing on another Observation subtype, the Event. To get the information about the day length we introduce a sun events.
You can see sample Event data here: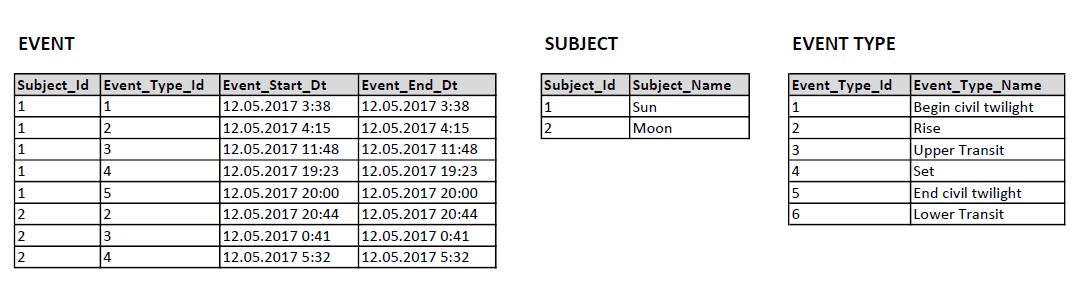
The whole table structure is available in public repository on GitHub here personal_dwh/tree/master/detail_layer/db/tables
Data source
As the source for event data we use public Astronomical Applications API provided by The United States Naval Observatory (USNO).
Here is sample URL requesting all Sun and Moon events for one day on location specified by coordinates: http://api.usno.navy.mil/rstt/oneday?date=05/12/2017&coords=48.749015N,16.983294E&tz=1
ETL environment
We use Google Apps Script as environment for data extraction, load and transformation (ETL) and also as job scheduler. It is used for building both detail layer in Cloud SQL and application layer in Firebase.
The data flow
The whole flow starts by loading the detail table Event
We have few views in Cloud SQL to support the detail layer load. They define the load scope. The default scope is limited by the beginning of our DWH and end of current year. Later the begining of the load scope moves according to already loaded data. You can see the view definitions here personal_dwh/tree/master/detail_layer/db/views. The detail layer load in SQL cloud is driven by the content of Event table itself.
The astronomical datamart is again defined as a view. There is not so big volume of data so all hourly, daily, monthly, yearly data is derived on top of one, hourly view v_ daylight_ length_ hourly.
All hourly, daily, monthly, yearly data is materialized in the Firebase. The load is driven by new control table t_ loaded_ periods. The range of data for the actual load is defined by views v_ load_ scope and v_ load_ range
The script for loading the astro events into detail layer is here pdwh_ detail_ event_ astro.gs
The script for building the access layer in Firebase is here firebs_ meas_ astro_ daylight.gs
Reporting tool
At the end we do small change in our web app to include the new data. The change takes place in one file data-view.html. The dropdown menus for Subject Area, Measure and Grain will be now dynamic, generated from associative arrays measureDict and grainDict.
The final result you can see here lubolab-957a1.firebaseapp.com. Login into your gmail account is required.